Have you ever had to spend hours manually entering data from handwritten forms or invoices? Or tried to decipher a doctor’s illegible handwriting? It’s very likely that your answer to this would be a yes and the formidable challenges associated with manual data extraction from handwritten forms and the deciphering of illegible handwriting extend beyond mere inconvenience; they can lead to substantial losses and grave compliance issues for enterprises. Inaccuracies arising from manual data entry errors can propagate through critical business processes, compromising decision-making, and potentially resulting in financial losses.
Historically, deciphering messy handwriting and manually inputting data from forms and invoices has been a labor-intensive and error-prone task. While Optical Character Recognition (OCR) was a significant advancement, OCR limitations become apparent in terms of precision and adaptability. This blog post delves into the evolution of automated document processing, highlighting the pivotal role played by Intelligent Character Recognition in overcoming OCR’s limitations. Additionally, we explore how ICR, in conjunction with Natural Language Processing (NLP), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Cognitive Process Automation (CPA), is ushering in a new era of efficiency and accuracy.
A glance at all that this article covers:
What is Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)?
At its core, Intelligent Character Recognition represents a formidable fusion of artificial intelligence and machine learning to form a revolutionary intelligent document processing solution. It harnesses the power of machine learning to enable computers to proficiently recognize and interpret multiple data formats, including handwritten text, surpassing the limitations of Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in terms of accuracy.
The Intelligent Character Recognition process begins by segmenting a document into individual characters through computer vision techniques, effectively identifying the boundaries that separate each character. Subsequently, Machine Learning algorithms, extensively trained on extensive datasets of handwritten text, come into play, allowing them to discern the diverse shapes and patterns of letters.
Adding another layer of proficiency, ICR also employs Natural Language Processing techniques, which help with grasping the contextual aspects of the text, including grammar and syntax. This contextual awareness proves invaluable in accurately identifying characters, even when they are penned in cursive styles or marred by noise, rendering ICR a potent tool for complex document data extraction.
The Limitations of OCR: A Predecessor’s Shortcomings
The limitations of OCR systems are primarily attributed to their dependence on well-defined rules to match dark and light patterns with the correct characters, such as letters and numbers. These systems excel in processing uniform, structured content but encounter challenges when confronted with non-uniform contents like handwritten text, various shapes, tables, lines, and QR codes, which fall beyond their scope.
Specifically, the drawbacks of OCR can be categorized into the following factors:
- Variability of Handwritten Text: Handwritten text exhibits significant variations in terms of character size, shape, and spacing, rendering it a formidable challenge for OCR systems to accurately recognize and transcribe.
- Noise in Handwritten Text: Handwritten content often carries noise in the form of smudges, scratches, and irregular handwriting styles. This noise further complicates OCR’s ability to achieve accurate recognition.
- Complexity of Documents: Certain documents, such as intricate forms and detailed contracts, possess a high level of complexity and contain extensive data. OCR systems may struggle to accurately extract and process all the data within these documents due to their intricate layouts and content structures.
Feature Detection in Intelligent Character Recognition
In the realm of Intelligent Character Recognition, feature detection plays a pivotal role. Also known as feature extraction, this technique focuses on dissecting the specific elements that compose individual characters rather than treating the character as a whole. Unlike pattern recognition, which relies on matching characters to predefined libraries, feature detection identifies unique characteristics that differentiate one character from another. For instance, when confronted with an ‘A’ characterized by two angular lines converging to a point and intersected by a horizontal line in the middle, ICR’s feature detection can reliably recognize it as an ‘A’, regardless of the font style. This approach grants ICR the flexibility to identify characters, even when encountering unfamiliar fonts, making it exceptionally robust in scenarios with challenging document conditions, such as faded ink or degraded images.
OCR vs Intelligent Character Recognition: A Comparative Analysis
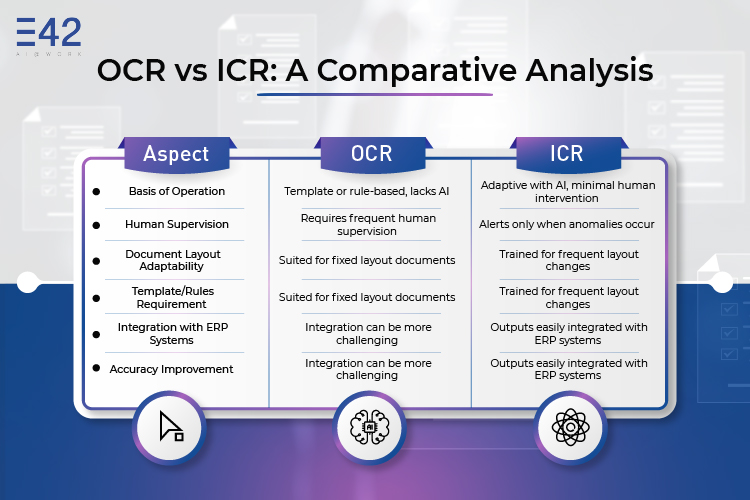
Intelligent Character Recognition’s Practical Applications
Intelligent Character Recognition has found valuable applications in various document processing scenarios:
- Automating Data Entry: ICR’s proficiency in deciphering handwritten forms and surveys eliminates the need for manual data entry, saving both time and ensuring precision.
- Streamlining Invoice and Receipt Processing: ICR simplifies the intricate process of processing invoices and receipts, reducing resource burden while elevating data accuracy.
- Processing Handwritten Notes and Annotations: In domains requiring the extraction of valuable information from handwritten notes and annotations, such as research documents or legal papers, ICR proves to be a reliable asset.
How does Intelligent Character RecognitionSurpass the Limitations of OCR?
Intelligent Character Recognition transcends OCR limitations in numerous aspects:
- Enhanced Precision: Thanks to its machine learning capabilities, ICR excels at deciphering even the most challenging handwritten texts, including those in cursive or marred by irregularities.
- Heightened Efficiency: ICR’s automation of tasks that were once manual not only reduces operational costs but also optimizes resource utilization and ensures data accuracy.
- Versatility: ICR’s adaptability allows it to extract data from a broad spectrum of document types, surpassing OCR’s limitations.
- Multilingual Support: ICR systems are engineered to scan and transform text content across various languages.
The integration of Intelligent character recognition into existing Document Management Systems (DMS) accelerates the entire document management process. Implementing Intelligent character recognition involves careful consideration of document types, precision requirements, budgetary considerations, and the depth of integration with existing systems. Striking a balance among these factors ensures the effective deployment of ICR.
Key Considerations for ICR Implementation
When implementing OCR and ICR technologies, it’s imperative to align them with your business requirements, necessitating a clear grasp of your objectives and expected benefits. Furthermore, in the context of ICR, due to its involvement with sensitive data, robust security measures are indispensable for preserving data integrity and privacy. Additionally, achieving optimal results with ICR models entails rigorous training on sizable handwritten text datasets, emphasizing the significance of fine-tuning to effectively meet specific business needs.
Conclusion
Intelligent Character Recognition represents a revolutionary leap in document processing, overcoming the limitations of OCR. Through a blend of AI, machine learning, and NLP, ICR excels in deciphering handwritten text and complex documents, streamlining data entry, and enhancing efficiency. Its advantages, including precision, efficiency, versatility, and multilingual support, make it invaluable. ICR’s integration into DMS accelerates processes, but careful implementation is essential. With ICR, powered by NLP, AI, and CPA, a new era of efficient and accurate document processing emerges, empowering businesses to make informed decisions and achieve success.
Streamline Your Enterprise Operations with E42
E42 is a no-code Cognitive Process Automation (CPA) platform that empowers businesses to create AI co-workers equipped with Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR) capabilities. These AI co-workers are adept at automating a wide range of business processes with remarkable speed and precision. Tailored specifically for the finance domain, our AI co-workers excel in handling critical tasks such as Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, financial reporting, and data extraction through ICR. Operating at an accelerated pace, these AI co-workers offer end-to-end process automation, delivering significant benefits to the finance team and the entire organization. Reach out to us at interact@e42.ai.



