Today, AI-powered automation is gaining widespread recognition, and for a good reason. It has made our lives easier. With the advent of virtual assistants, we’ve already experienced rudimentary AI via our ‘smart’ gadgets. A simple example would be an ‘Alexa’ or a ‘Siri’ – who can listen and converse with us by simply following a ‘wake word’. Another area where we all experience automation in our day-to-day lives is customer care. Be it our banking needs or fixing an issue with our mobile operator, we no more need to be queued up for minutes (or even hours) to get connected to customer care rep. Virtual assistants are there to not only attend to our simple queries but also resolve most of our not-so-complicated issues without any human intervention. Even though that is a technological leap compared to a decade ago, AI-based automation has evolved into so much more than just ‘bots’.
What is Cognitive Process Automation?
Cognitive process automation or intelligent automation is the process of putting intelligence into traditional process automation techniques by employing employs artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP). It enables enterprises to better capture data, automate decision-making, and scale automation. Unlike Robotic Process Automation (RPA) which works on simple if-then logic and can only handle structured data which is typically organized in enterprise systems, CRM, LMS, ERP, etc., CPA intelligently processes structured as well as unstructured data that includes voice, video, document repositories, URLs, and more. While RPA replaces the human to perform mundane, unintelligent tasks, Cognitive Process Automation puts the human in the robot – to handle complex data, bring out insights, make decisions, and much more.
Cognitive automation vs RPA: What’s the difference between the two?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
The thing to remember is that RPA, like RDA and Chatbots, is more of a first-gen technology. Its ability to handle high-volume tasks helps with simple business processes like data entry. Meaning that it has its limitations. For instance, RPA is process driven – it’s designed to offer choreographed, robotic repetition and generally malfunctions when dealing with inaccurate, unstructured, or blank data. In other words, it cannot problem-solve. When it hits a wall, human intervention is required to complete the task and watch for the subsequent breakdown.
Besides, RPA is best to be deployed in a stable environment with standardized and structured data. Meaning, RPA is typically programmed for back-office automation and especially excels at automating rules-based tasks that strictly follow if-then-else logic. It can be largely used to drive a degree of process efficiency and reduction in routine manual processing. Although it is able to drive significant value but isn’t incompatible with truly transformational change in enterprise functionality due to its inability to deal with complex decision-making tasks.
The other issue with RPA is the cost. It would cost an organization a significant sum to build or outsource the technical know-how required to automate each process individually. This could take months to accomplish. Not to mention, the desired results depend on the entire process remaining the same for all that time. Any change, however minute, could result in additional expense and development.
Cognitive Process Automation
Cognitive Process Automation is built on AI-based human-like thinking. Hence, CPA-powered AI solutions can be implemented to handle complex employee and customer-centric tasks. This can automate a variety of tasks across enterprise processes including HR, sales and marketing, IT operations, customer service, finance, and more including lead creation, discovery, support, ticket generation, leave application and approval, and much more. With CPA, it’s possible to manage all this in natural language using an omnichannel interface across the web, WhatsApp, Teams, and more.
It’s suitable for a complex IT environment with non-standardized and unstructured data as it can efficiently turn any data gathered from documents, customer interactions, or voice into an efficient business workflow. In other words, CPA helps bridge the gaps between RPA chatbots, low-code applications, and programming interfaces.
Cognitive Process Automation is great for deriving meaningful conclusions from unstructured data. Most business processes can be automated resulting in an organization’s improved efficiency, especially in customer-facing processes, given the importance of capturing and understanding users’ requirements and feedback. Furthermore, it blends a variety of AI techniques such as NLU, sentiment analysis, image identification, and intelligent data extraction to analyze huge volumes of information around complex business tasks in a way that mimics human thought and decision-making – making it seamless for businesses to adapt quickly and act on new patterns and insights.
How Does Cognitive Automation Help in Coping with the Limitations of RPA?
Much of the confusion around RPA and cognitive automation comes from the fact that they are closely related to each other and in many areas, have worked hand in hand. These technologies are two ends of the same intelligent automation.
Scope
Traditional automation and RPA can only be used to automate repetitive, mechanical, straightforward, and mundane tasks which follow a rigid set of rules and hardly require analysis or thinking. Cognitive automation, on the other hand, is all about bringing automation to major enterprise processes that require a certain level of decision-making, human-like judgment, intelligence, and insights. It enables machines to complement the human workforce when it comes to tasks or processes that involve challenging amounts of data to be processed, monitored, and analyzed with specific business objectives.
The type of data processed
In today’s world, data is at the core of any business, data that comes in various forms. An organization that’s not employing ways to harness it is sure to lag in the cut-throat competition. It can be organized in a predefined format, say a database or spreadsheet with rows and columns – known as structured data. This kind of data can be easily handled and hence, automated using RPA – for the obvious reason that it doesn’t require intelligence to be processed. However, a major chunk of enterprise is classified as unstructured data – from videos to audio files, images, web URLs, and more – stuff that cannot be processed by RPA. This is where cognitive process automation tools play the role of bringing in the intelligence that it takes to make sense of this enormous amount of data – reducing human intervention, augmenting speed and accuracy, and enabling enterprises to achieve a superior level of intelligent business automation.
Automation method
RPA typically is applied to automate processes that require decisions that follow a simple if/then logic – to eliminate the manual effort from time-consuming tasks that need rapid and monotonous step-by-step actions. Cognitive process automation on the other hand, enables machines to make human-like conversations and make decisions as a result of AI and NLP-led training that they go through to learn human behavior and comprehend information in various formats including but not limited to voice and video.
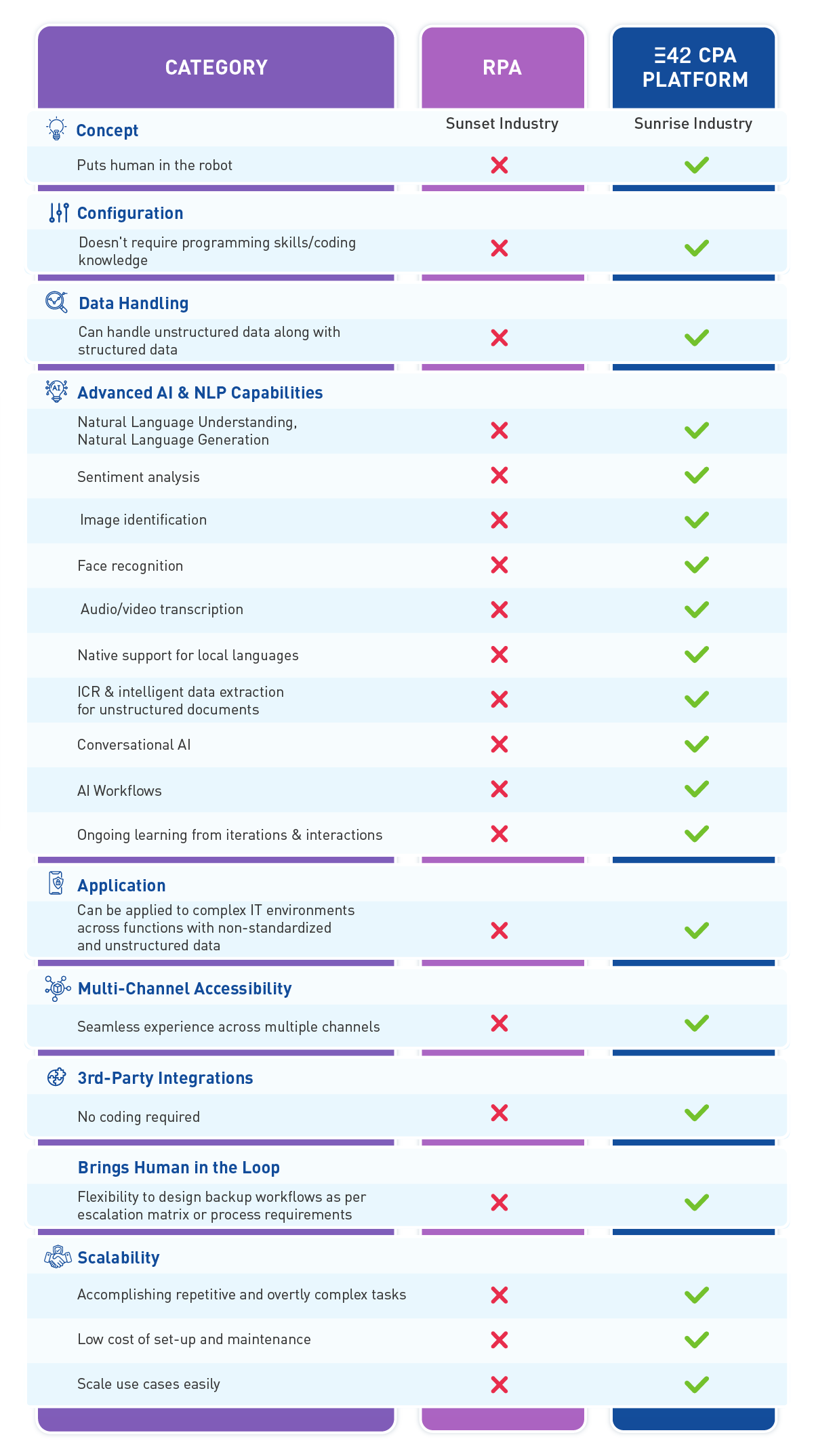
In simple terms, AI co-workers configured using CPA can think, reason, and perform activities like humans but on both structured and unstructured data with better accuracy and speed. RPA and other traditional bots on the other hand need to be told what to do and can only follow a set of instructions, processing only structured data. Without specific instructions, which is impossible in the case of complex processes involving a volume of unstructured data, RPA can malfunction or even crumble, hence limiting its application. But, as humans, what do we do when faced with incomplete instructions or information? We problem-solve, learn, adapt, and grow. That’s exactly what CPA does, and it does so more efficiently!
Conclusion
RPA helps organizations reduce back-office costs and increase productivity by performing basic tasks with greater precision and accuracy. While some of the mundane processes can be automated using RPA, complex tasks require context, judgment, prediction, and an ability to learn. Cognitive automation tools use AI techniques in places where document processing, vision, natural language, and sound are required, taking automation to the next level – allowing humans to sit back and let the machines do the work. Additionally, it gives enterprises the ability to foresee and continuously bring process improvements in response to changes, trends, patterns, and more!
Intelligently Automate Your Business Processes with E42
E42 is a no-code Cognitive Process Automation platform that offers enterprises the ability to implement various AI co-workers irrespective of their line of business to automate complex tasks or processes. These AI co-workers could be customized accordingly to help businesses solve a particular problem area across verticals and functions. The most integral component of these AI co-workers is that they can think like humans, predict customer behavior, understand user sentiments, take charge based on analysis, as well as learn from each interaction. These AI co-workers can work independently or can be clubbed with other AI co-workers in the fields of HR, finance, IT, customer care, and more – bringing process-agnostic automation to enterprises!



