Artificial intelligence (AI) has transitioned from a futuristic concept to an integral component of modern technology, revolutionizing industries and reshaping the world as we know it. However, AI is not a monolithic field—it comprises various subfields, each with distinct applications and implications. Among these, Explainable AI (XAI), generative AI, Edge AI, agentic AI and human-AI collaboration stand out as pivotal concepts that are driving advancements in both business and society.
This article will dive into these AI branches, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance and their role in shaping the future of intelligent systems.
1. Explainable AI (XAI): Shedding Light on the ‘Black Box
As AI systems grow more complex, one of the critical challenges is understanding how these systems make decisions. Traditionally, machine learning models, particularly deep learning networks, have been regarded as ‘black boxes’—they produce highly accurate predictions, but the rationale behind those predictions is often opaque. This lack of transparency has been a barrier to the wider adoption of AI, especially in sectors like healthcare, finance, and law, where accountability is critical.
Explainable AI (XAI) addresses this challenge by making AI systems more interpretable and transparent. XAI methodologies enable developers and end-users to understand, trust, and manage AI systems by providing clear insights into how an AI model reaches its conclusions. These explanations can range from simple feature importance rankings to more sophisticated techniques like local surrogate models or SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) values, which offer a more granular understanding of model behavior.
For example, in healthcare, where AI is used to predict patient outcomes, doctors need to know why a specific decision was made. XAI ensures that they can trace the decision back to specific data points, improving trust and ensuring that AI augments human expertise rather than obscures it.
2. Generative AI: Creating More Than Predicting
Generative AI and its use cases is an exciting and rapidly advancing area of artificial intelligence that’s reshaping various industries. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on making predictions or classifications, what generative AI does is that it creates new content—whether it’s text, images, music, or even virtual environments. Its applications span across multiple fields: in content creation, it’s helping draft articles and generate product descriptions; in healthcare, it’s designing new molecular structures for drug discovery; and in design, it’s sparking creativity in fashion and architecture by generating unique outputs based on specific parameters.
3. Edge AI: Intelligence at the Source
As the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices increases, there is a growing need for processing power closer to the data source. Traditionally, data collected by IoT devices is sent to the cloud for analysis, but this can result in latency issues and higher costs associated with data transmission. This is where Edge AI use cases comes into play.
Edge AI refers to the deployment of AI algorithms directly on devices at the ‘edge’ of the network, close to where data is generated. Instead of relying on the cloud, edge devices such as sensors, drones, or cameras can process data locally, making real-time decisions based on AI insights.
The advantages of Edge AI are numerous:
- Low Latency: For real-time applications like autonomous vehicles or industrial robotics, decisions must be made in milliseconds. Edge AI ensures that data doesn’t need to travel back to the cloud, reducing delays and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced Privacy: Sensitive data can be processed locally, minimizing the need to transmit information across the network, reducing the risk of breaches.
- Cost Efficiency: By processing data at the source, businesses can significantly reduce bandwidth and cloud storage costs.
An example of Edge AI in action is in smart cities, where traffic cameras can use AI to analyze real-time data, adjust traffic signals, and improve urban mobility—all without requiring cloud connectivity. In industries like manufacturing, Edge AI systems can predict equipment failures in real-time, enabling preventive maintenance and reducing downtime.
4. Agentic AI: Towards Autonomous Decision-Making
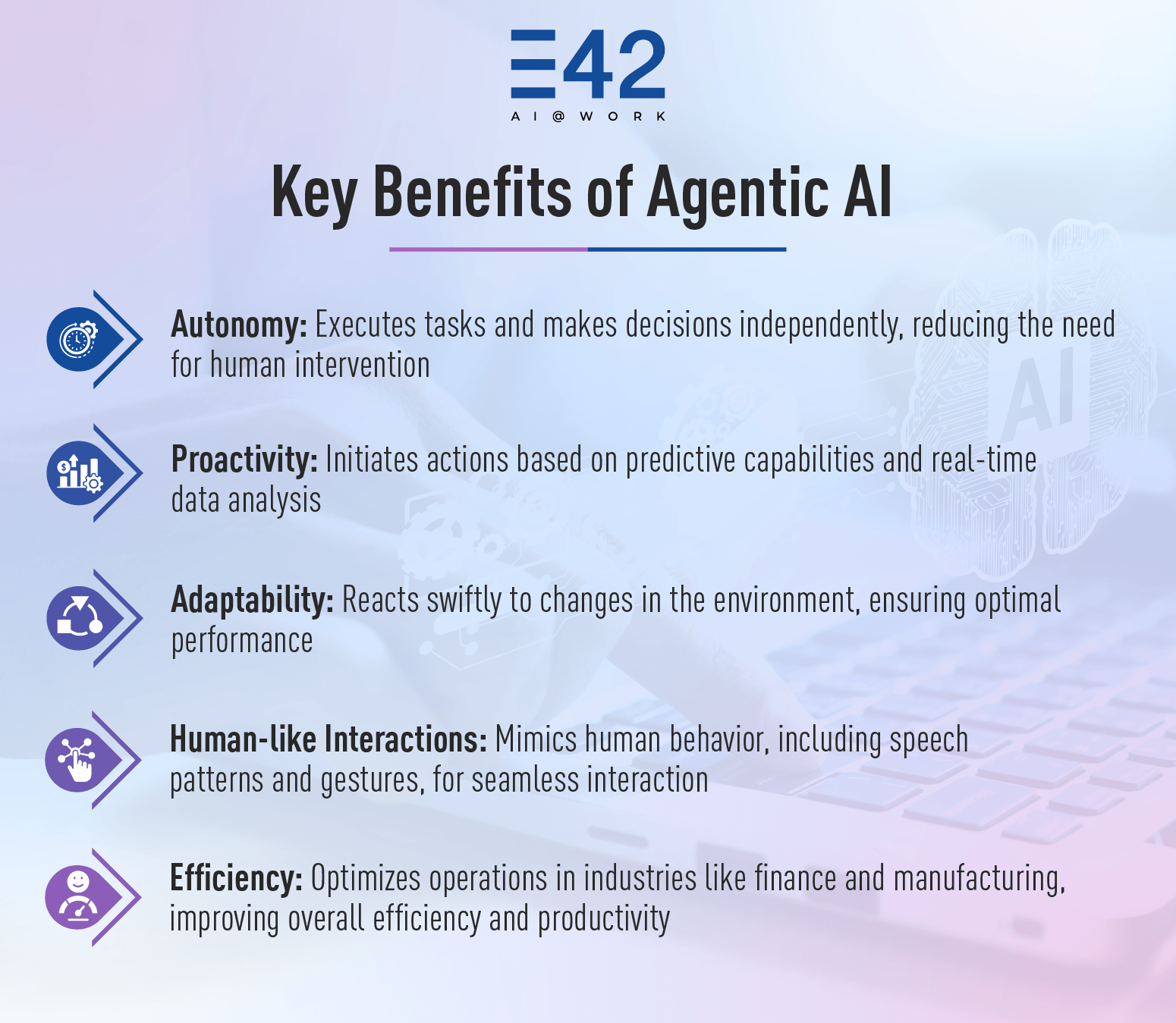
Agentic AI represents a significant leap in artificial intelligence, where systems go beyond executing tasks to act autonomously, make informed decisions based on predefined goals and real-time environmental inputs, and interact seamlessly with other agents and humans. Unlike traditional AI, what agentic AI does is that it demonstrates autonomy, proactively initiating actions, predictive capabilities to anticipate outcomes, and reactivity to adapt swiftly to changes.
These agents are designed to mimic human-like behavior, including speech patterns, gestures, and attitudes, making them appear as real human beings. They can provide human-like interactions with real-time gestures and attitudes. This makes it ideal for industries like finance, where AI agents can autonomously execute trades by analyzing market data in real time, or manufacturing, where they optimize operations without human intervention.
5. Human-AI Collaboration: A Symbiotic Relationship
While the narrative around AI often centers on the fear of machines replacing humans, the future of AI is more collaborative than competitive. Human-AI collaboration emphasizes the synergy between human intelligence and artificial intelligence, where each enhances the other’s strengths.
In human-AI collaboration, AI solutions like AI co-workers work in tandem with each other and handle data-intensive tasks, allowing humans to focus on creativity, strategy, and decision-making.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of AI
As AI technologies continue to evolve, understanding the distinct branches of AI—XAI, generative AI, Edge AI, agentic AI and human-AI collaboration—becomes crucial for businesses looking to innovate responsibly and effectively. AI is not just transforming industries—it’s augmenting humanity’s ability to solve complex problems and shape a better world.



