In 2023, along with the rise of generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) the digital world faced unprecedented challenges as the average cost of a data breach soared to a staggering $4.45 million. With cyberattacks happening at an alarming rate of over 2,200 per day, businesses are under immense pressure to protect their digital assets. The rise in cyber threats, coupled with a 38% increase in attack volume, underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. As enterprises increasingly depend on data to fuel innovation and decision-making, the stakes are higher than ever. The advent of generative AI and LLMs further complicates the scenario, raising crucial questions about safeguarding sensitive information in this rapidly changing environment. The urgency for responsible AI, which emphasizes the importance of ethics and privacy in AI, has never been greater.
The Rising Tide of AI-Driven Cyber Threats
As technology advances, so does the complexity and danger of cyber threats. A recent instance involved AI-generated deepfake videos of political leaders making controversial statements, which went viral on social media and caused widespread public outrage before being debunked. This incident highlighted the growing threat of AI-driven misinformation and its potential to disrupt social and political stability. But this is just scratching the surface. The rise of generative AI also brings critical concerns about ethics and privacy in AI, as these technologies can be exploited to invade personal privacy and manipulate public opinion.
Advanced AI Attack Vectors:

- Deepfake Technology: AI-generated deepfakes are increasingly being used to create realistic but fake identities for fraudulent purposes. Criminals have begun leveraging this technology to fabricate KYC (Know Your Customer) documents, allowing them to open bank accounts or secure loans under false identities. These AI-generated faces and voices can be nearly indistinguishable from the real thing, making detection incredibly challenging.
- Voice Phishing (Vishing): Generative AI is also being used to replicate voices with startling accuracy, leading to sophisticated vishing attacks. In some instances, AI-generated voices have been used to impersonate executives, instructing employees to transfer large sums of money or disclose sensitive information, leading to substantial financial losses.
- AI-Powered Social Engineering: With the help of LLMs, attackers can craft highly personalized and convincing phishing emails that are tailored to the specific behaviors and preferences of the target. These emails can be so convincing that even the most vigilant employees might fall prey to them.
- Automated Vulnerability Scanning: AI can be used to automatically scan for vulnerabilities in software systems by analyzing codebases, especially those of open-source projects. Once a vulnerability is identified, attackers can quickly develop exploits, leaving organizations with little time to respond.
- Malware Enhancement: AI can refine malware to slip past traditional security systems. For instance, machine learning algorithms can enable malware to adjust its behavior on the fly, evading common detection techniques such as signature-based antivirus systems.
Addressing Privacy and Ethics Concerns in the AI Era
Ensuring ethics and privacy in today’s AI-driven world requires a strategic, multifaceted approach. Enterprises must navigate the fine line between leveraging AI for innovation and protecting individual privacy rights. To do so, they must focus on the following key strategies:
- Responsible Data Collection and Analysis: AI models like LLMs are built on vast datasets that often include personal information. To prevent unintended disclosure of sensitive data, it is crucial to implement strong privacy controls and ensure that AI models do not inadvertently expose personal information.
- Proactive Threat Management: Utilizing Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) and Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SSDLC) frameworks is essential for identifying and mitigating data security risks. These tools help to safeguard AI models from vulnerabilities such as prompt injection and toxicity.
- Ethical AI Practices: AI systems must be designed to mitigate biases that may exist in training data. Addressing these biases is essential to maintain transparency and fairness in AI deployments, ensuring that the benefits of AI are realized without compromising ethical standards.
- Compliance with Global Data Regulations: As with all digital technologies, AI models must adhere to data protection regulations, such as the GDPR. This involves anonymizing and de-identifying data to protect user privacy and comply with legal requirements.
- Applying Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation: Data minimization ensures that only the necessary amount of data is used for AI model training, while purpose limitation guarantees that data is only utilized for its intended purpose. These principles are crucial for protecting ethics and privacy in AI applications.
Constructing a Robust Data Defense System
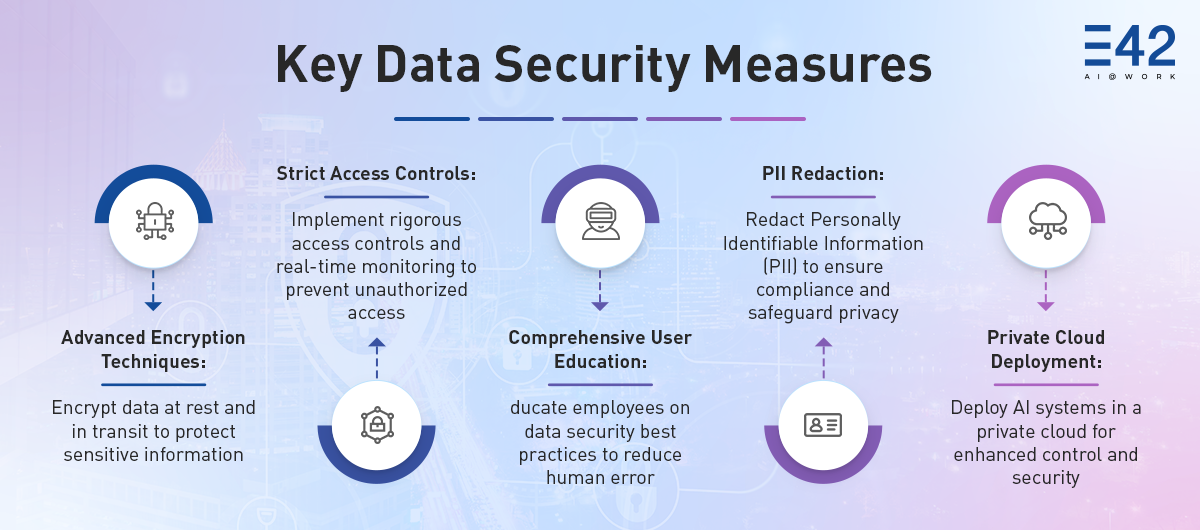
Building a resilient data security infrastructure using AI requires more than just implementing technical solutions—it demands a strategic and holistic approach. Key components of this strategy include:
- Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is essential for protecting sensitive information, safeguarding data confidentiality and integrity, even in the event of a breach.
- Strict Access Controls: Implementing rigorous access controls and real-time monitoring systems can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, thus enhancing the overall security posture of an organization.
- Comprehensive User Education: With the rise of LLMs, educating employees on best practices for data security while using AI is vital for reducing human error and enhancing the effectiveness of security measures. This indicates the utmost importance that user awareness and training hold to ensure a robust security strategy.
- PII Redaction: Redacting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is a crucial step in ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and safeguarding user privacy, particularly in industries that handle sensitive data.
- Private Cloud Deployment: Deploying AI systems in a private cloud environment offers enhanced control and security, making it a preferred option for industries with stringent data protection needs.
Conclusion: Securing the Future in the Age of AI
As we delve deeper into the age of generative AI and LLMs, it becomes increasingly clear that data security is not just about protecting information—it is about ensuring the responsible use of technology. The advancements in AI offer incredible opportunities for innovation, but they also introduce significant risks that must be managed proactively. By adopting a comprehensive and strategic approach to data security and responsible AI, enterprises can not only protect their critical digital assets but also uphold the values of ethical AI deployment. In doing so, they pave the way for a future where technology drives positive change and sustainable growth.
To discover how to effectively leverage AI for your enterprise without compromising on security, write to us at interact@e42.ai.



